Empathy Map
Intermediate
60 minutes
Get the tool.
Read our data policy >Get to know what motivates your user.
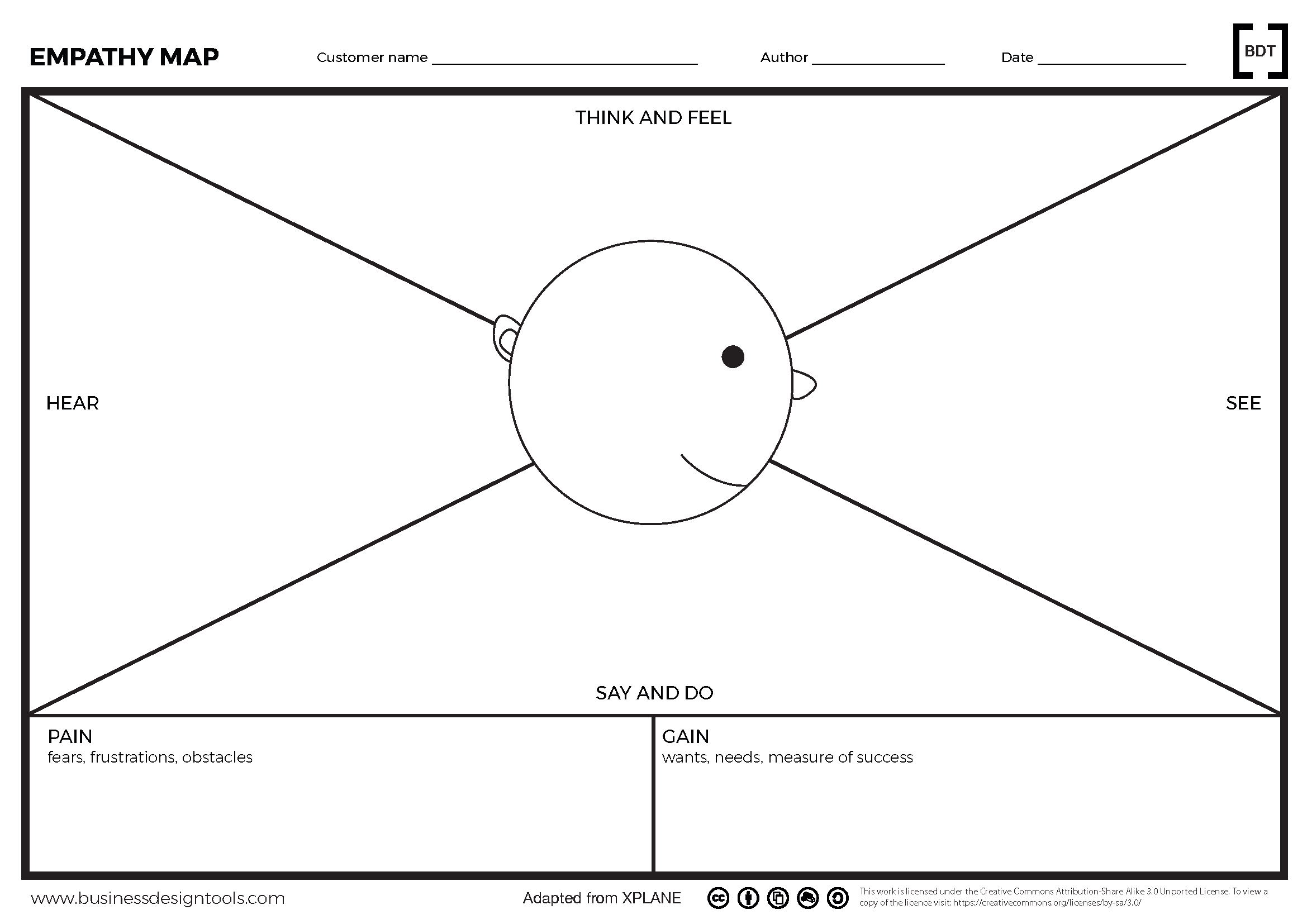
The Empathy Map is a strategy tool that helps entrepreneurs gain a deep understanding of their target customers.
The advantages of using an Empathy Map are significant. First and foremost, it promotes a customer-centric approach. By understanding the true needs of their customers, organizations can create products and services that enhance satisfaction and loyalty. This deep understanding also aids in strategic decision-making, allowing teams to prioritize features and allocate resources more effectively. Furthermore, insights gained from empathy mapping can differentiate a business in the market, enabling them to develop innovative solutions that stand out from competitors.
To utilize the Empathy Map effectively, businesses should start with clear objectives, defining what they aim to learn about their customers. Basing insights on real data collected through customer research is essential for accuracy. Making the map visible across teams ensures that everyone shares a consistent understanding of customer insights. Regular reviews of the map help incorporate new information as it becomes available, and connecting insights to actionable decisions is vital for driving business forward.
Step-by-Step
Complete the Empathy Map
Use this checklist to complete the canvas.
Gather Your User Research
Collect all available customer data, including:
- User interviews
- Survey responses
- Customer feedback
- Support tickets
- Market research
- Analytics data
- Social media insights
Decide on Your Mapping Strategy
2.1 Beginning from Emotions
- Start with core emotional states
- Map emotional triggers
- Document emotional responses
- Note intensity levels
- Connect emotions to behaviors
2.2 Beginning from Pains and Gains
- List key customer problems
- Document desired outcomes
- Map current workarounds
- Note aspirations and goals
- Identify opportunities
2.3 Pick Your Tool
- Physical options:
- Printed template
- Whiteboard & sticky notes
- Digital options:
- Online collaboration tools
- Digital whiteboard
- Spreadsheet template
Mapping the Four Quadrants
3.1 Thinks and Feels
- Document internal thoughts
- Map emotional responses
- Note aspirations
- List worries and concerns
- Identify values
3.2 Hears
- What do they hear from:
- Friends and family
- Colleagues
- Social media
- Traditional media
- Industry influences
3.3 Sees
- What do they observe in:
- Their environment
- The marketplace
- Their peers’ behavior
- Media and advertising
- Product offerings
3.4 Says and Does
- Document stated opinions
- Record observed behaviors
- Note public actions
- List social media activity
- Identify contradictions
Mapping Pains and Gains
Pains
- List frustrations
- Document obstacles
- Note fears
- Map challenges
- Record risks
Gains
- Identify desires
- List success metrics
- Map aspirations
- Note ideal outcomes
- Document needs
Putting It All Together
5.1 Apply to Business Model Canvas
- Connect insights to:
- Value propositions — What does your user care about? What do they need?
- Customer segments — What does the Empathy Map tell you about the user segments you should focus on?
- Customer relationships — How can you better connect with your user, considering what the Empathy Map has revealed?
- Channels — What channels matter to your user?
5.2 Apply to Persona Canvas
- Integrate findings into:
- Demographics — What does the Empathy Map reveal about the user’s identity?
- Behaviors — What can the Empathy Map tell you about how the user behaves?
- Goals — How do the users thoughts and actions relate to their goals?
- Pain points & Motivations
5.3 Apply to Customer Journey Map
- Map insights across:
- Journey stages — What does the customer see, hear, think and do at different stages of the customer journey?
- Touchpoints — Consider what you’ve discovered from the See/Hear quadrants. What touchpoints are part of the customer journey?
- Emotional states — How does the customer feel as they navigate the customer journey?
- Pain points — How do their pain points map to different points of the customer journey?
- Opportunities — What opportunities have you uncovered when completing the Empathy Map? How do they relate to the customer journey?
Best practices
Do's
– Use actual customer quotes when available
– Be specific and detailed
– Include both emotional and rational aspects
– Focus on one customer type at a time
– Update regularly with new insights
Don'ts
– Don’t make assumptions without evidence
– Don’t mix different customer segments
– Don’t rush through the sections
– Don’t ignore contradictions
– Don’t skip any sections
Table of Contents
Updated January 16, 2023
More about the Empathy Map
The Empathy Map, originally developed by XPLANE, is a strategic tool that helps entrepreneurs gain a deep understanding of their target customers by visualizing user attitudes and behaviors. Unlike traditional market research tools, the Empathy Map encourages businesses to step into their customers’ shoes and view experiences from their perspective, leading to more empathetic and effective solution development.
The Power of Empathy Mapping
Empathy mapping offers several key benefits for businesses:
- Customer-Centric Approach: Enables organizations to develop products and services that genuinely address customer needs, fostering higher satisfaction and loyalty.
- Strategic Decision Making: Helps teams make informed decisions based on deep customer understanding, improving feature prioritization and resource allocation.
- Market Differentiation: Provides insights that allow businesses to create innovative solutions that stand out from competitors.
Using the Empathy Map Effectively
To maximize the value of your Empathy Map:
- Start with Clear Objectives: Define what you want to learn about your customers
- Use Real Data: Base insights on actual customer research whenever possible
- Make it Visible: Share the map across teams to ensure consistent understanding
- Review Regularly: Update as new customer insights emerge
- Connect to Action: Use insights to drive concrete business decisions
Core Components of the Empathy Map
Cognitive and Sensory Quadrants
- Think and Feel
- Internal thoughts and emotions
- Motivations and aspirations
- Concerns and worries
- Personal values and beliefs
- Hear
- Information sources
- Influential conversations
- Media exposure
- Word-of-mouth feedback
- See
- Environmental influences
- Competitor offerings
- Market trends
- Visual touchpoints
- Say and Do
- Verbal expressions
- Public behavior
- Actions and decisions
- Purchase patterns
Customer Value Analysis
Pain Points
- Challenges and frustrations
- Obstacles and barriers
- Risks and fears
- Negative experiences
Gains
- Desired benefits
- Success metrics
- Aspirations
- Expected outcomes
Types of Empathy Maps
Different situations call for different approaches to empathy mapping:
Individual Customer Maps
- Focus on specific user personas
- Detailed personal insights
- Useful for targeted product development
Segment-Based Maps
- Represent broader customer groups
- Aggregate common patterns
- Guide strategic planning
Project-Specific Maps
- Tailored to particular initiatives
- Focus on relevant behaviors
- Support specific design decisions
Best Practices for Using the Empathy Map
Creation Process
- Gather Data: Collect information through:
- Customer interviews
- Observation
- Surveys
- Social media analysis
- Customer feedback
- Organize Insights:
- Sort information into appropriate quadrants
- Identify patterns and themes
- Highlight key findings
- Update Regularly:
- Review and refresh content periodically
- Incorporate new customer insights
- Adjust based on market changes
Implementation Guidelines
- Keep it Focused:
- Concentrate on one customer segment at a time
- Maintain clarity and specificity
- Avoid generalizations
- Make it Collaborative:
- Involve cross-functional teams
- Share insights across departments
- Encourage diverse perspectives
- Use it Actively:
- Reference during decision-making
- Guide product development
- Inform marketing strategies
Conclusion
The Empathy Map is a powerful tool for developing deep customer understanding and creating more effective business solutions. By systematically exploring what customers think, feel, see, hear, say, and do, businesses can better align their offerings with customer needs and expectations. Whether used in product development, service design, or marketing strategy, the Empathy Map helps ensure customer perspectives remain central to business decisions.
Note: This guide builds on concepts developed by XPLANE and enhanced through design thinking practices. The structure and application may vary based on specific business needs and contexts.
References
Academic Sources
- Gray, D., Brown, S., & Macanufo, J. (2010). Gamestorming: A Playbook for Innovators, Rulebreakers, and Changemakers. O’Reilly Media.
- Brown, T. (2008). Design thinking. Harvard Business Review, 86(6), 84-92.
- Patnaik, D. (2009). Wired to care: How companies prosper when they create widespread empathy. FT Press.
- Mootee, I. (2013). Design thinking for strategic innovation: What they can’t teach you at business or design school. Wiley.
- Leonard, D., & Rayport, J. F. (1997). Spark innovation through empathic design. Harvard Business Review, 75(6), 102-115.
Industry Resources
- XPLANE. (2017). Empathy Map Canvas. Available at: www.xplane.com/empathy-map
- Gibbons, S. (2018). Empathy Mapping: The First Step in Design Thinking. Nielsen Norman Group.
- Dam, R., & Siang, T. (2020). Empathy Map – Why and How to Use It. Interaction Design Foundation.
Design Thinking and Research Methods
- Kumar, V. (2012). 101 Design Methods: A Structured Approach for Driving Innovation in Your Organization. Wiley.
- Martin, R. L. (2009). The Design of Business: Why Design Thinking is the Next Competitive Advantage. Harvard Business Press.
- Kolko, J. (2014). Well-designed: How to use empathy to create products people love. Harvard Business Review Press.
- Stickdorn, M., & Schneider, J. (2012). This is Service Design Thinking: Basics, Tools, Cases. Wiley.
Related Tools and Methodologies
- Pruitt, J., & Adlin, T. (2010). The Persona Lifecycle: Keeping People in Mind Throughout Product Design. Morgan Kaufmann.
- Young, I. (2015). Practical Empathy: For Collaboration and Creativity in Your Work. Rosenfeld Media.
- Bland, D. J., & Osterwalder, A. (2019). Testing Business Ideas: A Field Guide for Rapid Experimentation. Wiley.
Note: These references provide comprehensive coverage of empathy mapping and related design thinking methodologies. Some resources may have updated editions available.
Other tools

Affinity Mapping
Affinity Mapping enables teams to organize and make sense of complex information, ideas, and insights.
60 minutes
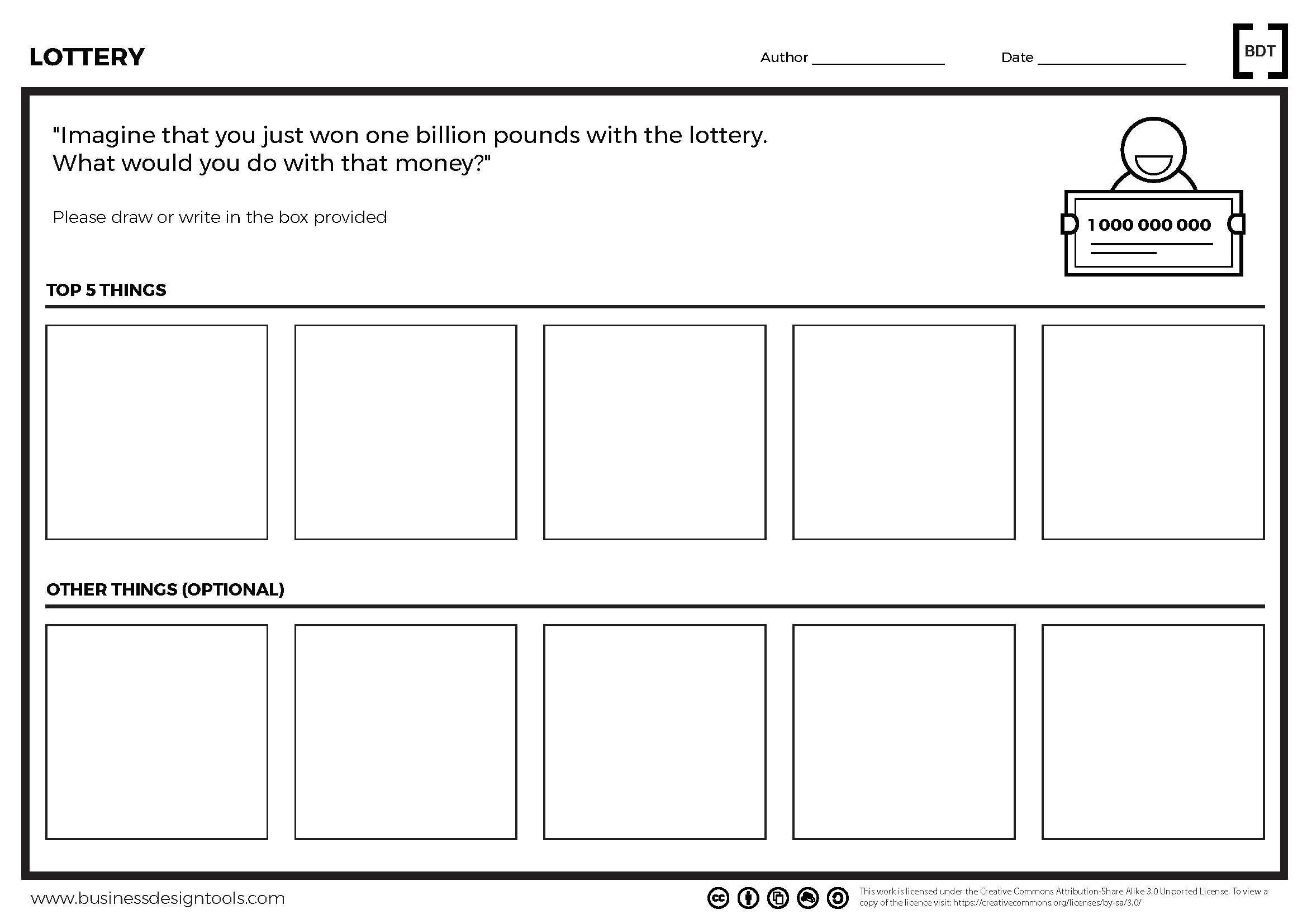
Lottery Canvas
The Lottery Canvas is a unique business strategy tool that allows entrepreneurs to explore their aspirations and priorities through a creative exercise.
30 minutes
PDF available
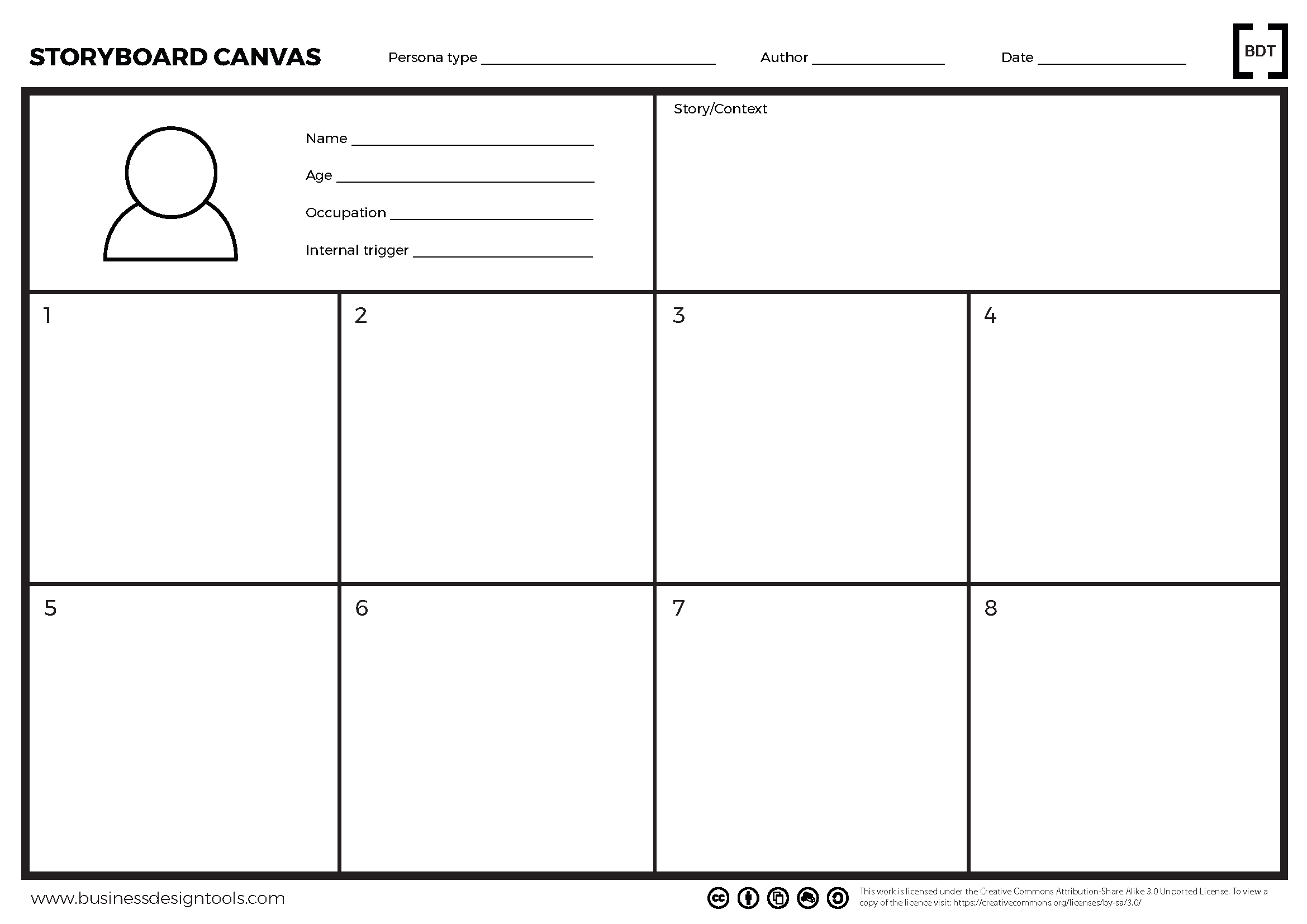
Storyboards
Uncover the narrative driving your product’s success using the storytelling method favored by Hollywood blockbusters.